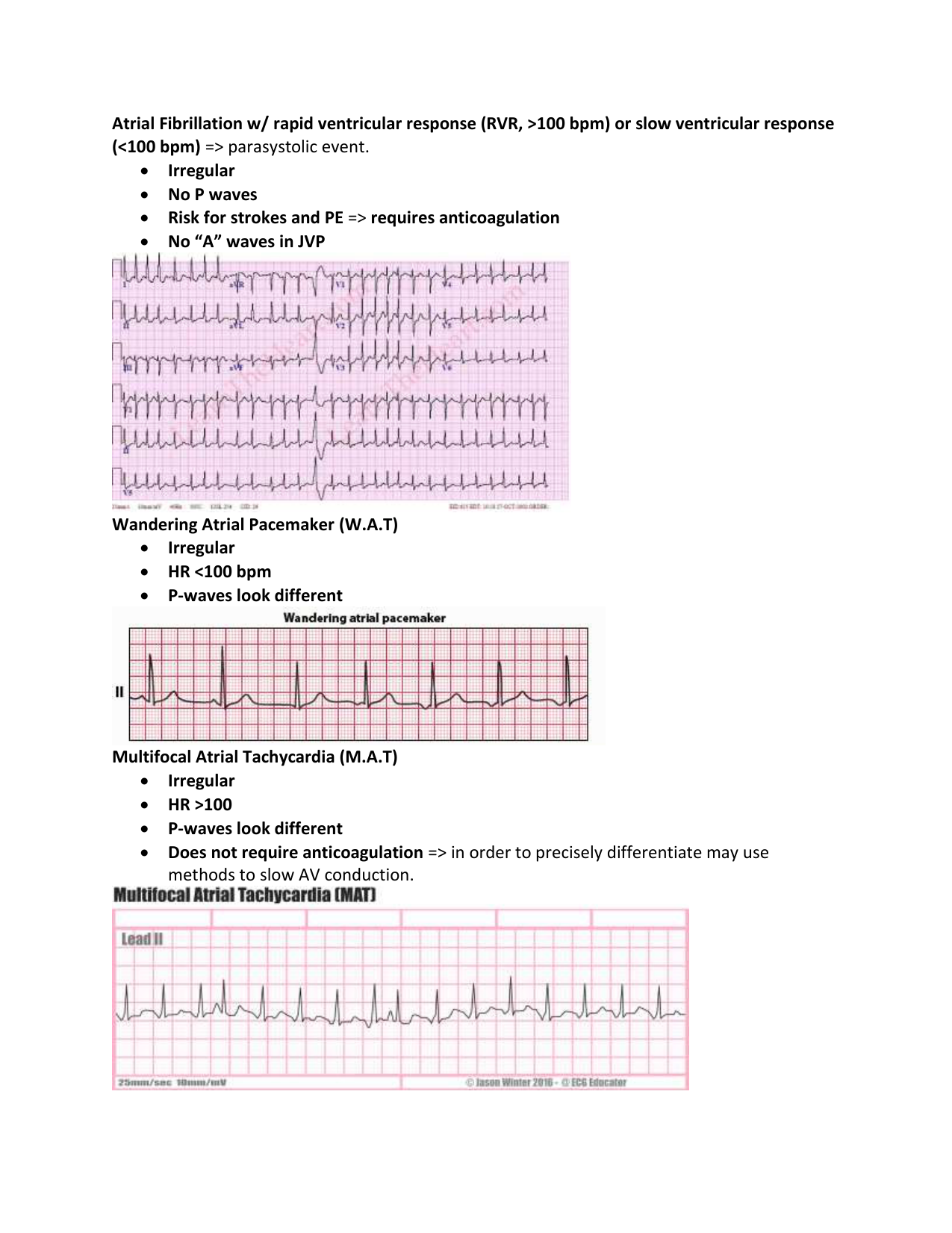
[10000印刷√] sinus rhythm with pjc ecg strip 311274-How to identify sinus rhythm on ecg
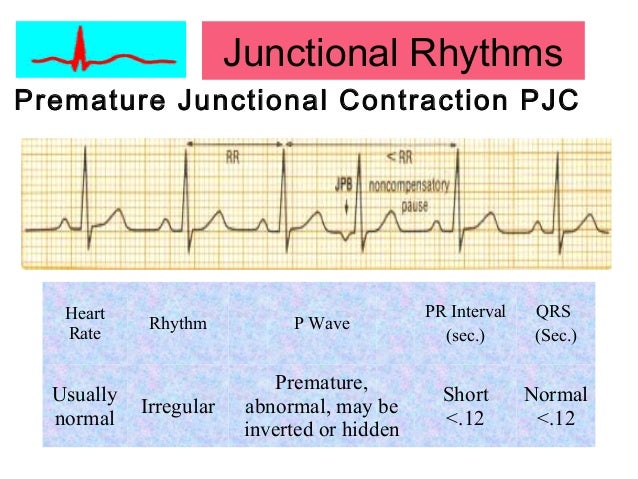
Junctional (escape) rhythm 40 60 bpm Accelerated junctional rhythm 61 – 100 bpm Junctional tachycardia >100 bpm Premature junctional complexes (PJCs)Sinus arrest with a PAC, Sinus bradycardia, 21 Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs) ECG Review Aug 15, d, 13 November 16, there is a pattern to this rhythm — in that "group beating" is present, Sinus rhythm trigeminal PACs, d, This could be mistaken for a ventricular ectopic — however, they may lead to a more serious atrial dysrhythmias, PJC), but may be aberrantlyApr 28, 21 · As you can see, a printed ECG rhythm strip is comprised of boxes – both small boxes and large boxes 5 small boxes make up one large box Each small box is 1mm wide, signifying 004 seconds or 40 milliseconds (ms) Each large box is 5 small
Ekg Flash Cards Pdf Rhythm Ecg Characteristics Normal Sinus Rhythm Nsr Rate 60 100 Per Minute Rhythm R R P Waves Upright Similar P R 0 12 0 Course Hero
How to identify sinus rhythm on ecg
How to identify sinus rhythm on ecg-Sinus bradycardia ECG, causes & management Definition of sinus bradycardia Sinus bradycardia fulfills the criteria for sinus rhythm but the heart rate is slower than 50 beats per minute ECG criteria follows Regular rhythm with ventricular rate slower than 50 beats per minute Pwaves with constant morphology preceding every QRS complexMar 11, 21 · ECG features of normal sinus rhythm Regular rhythm at a rate of bpm (or ageappropriate rate in children) Each QRS complex is preceded by a normal P wave Normal P wave axis P waves upright in leads I and II, inverted in aVR The PR interval remains constant




Ekg Flash Cards Pdf Rhythm Ecg Characteristics Normal Sinus Rhythm Nsr Rate 60 100 Per Minute Rhythm R R P Waves Upright Similar P R 0 12 0 Course Hero
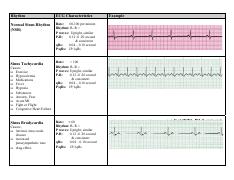
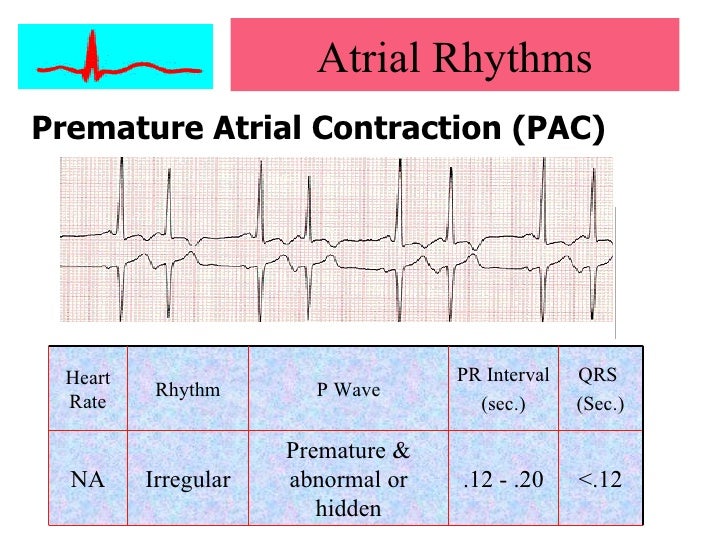
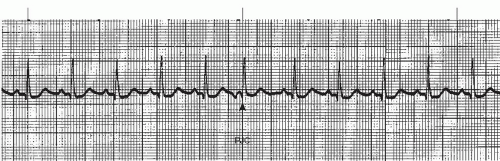
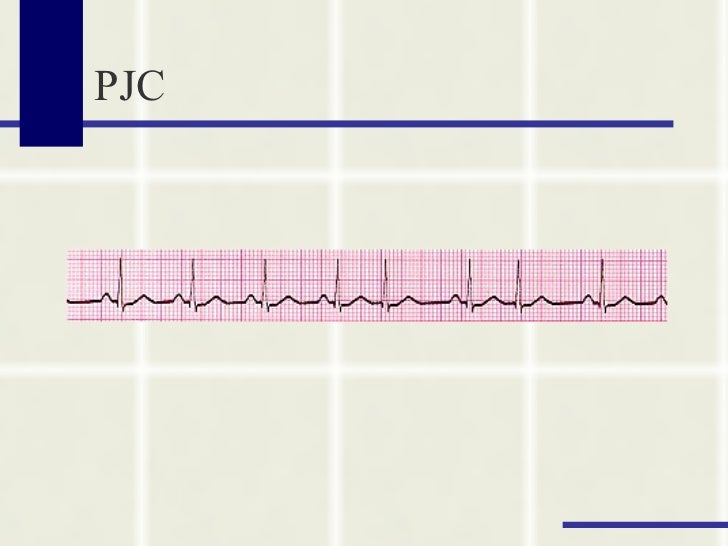
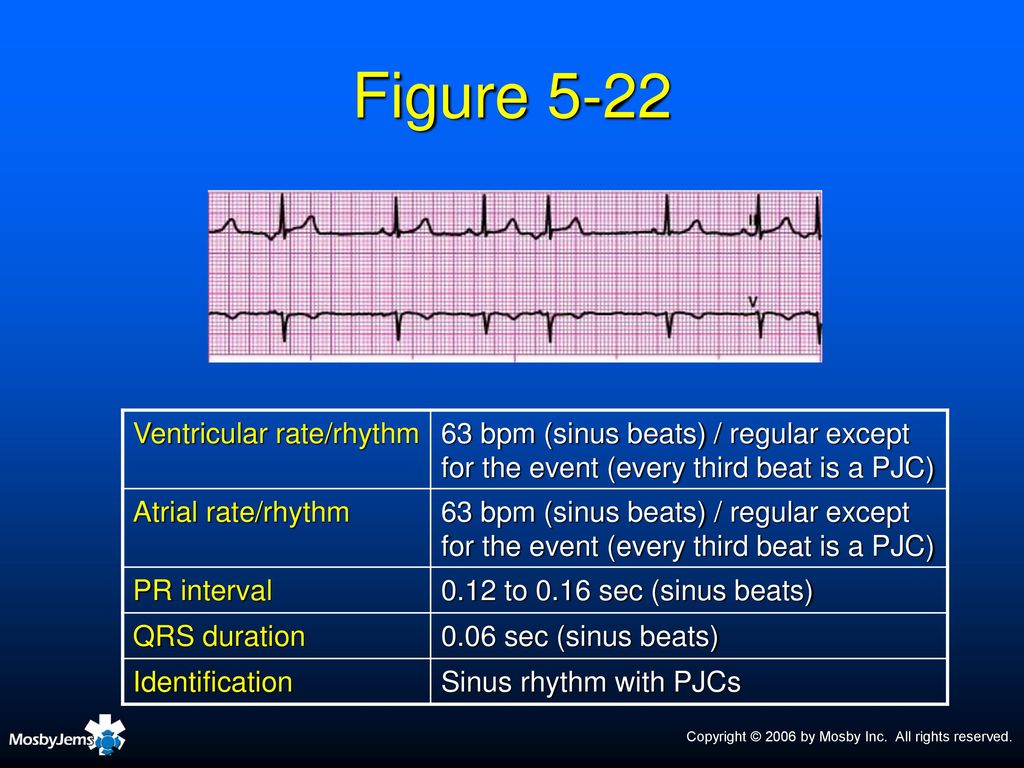
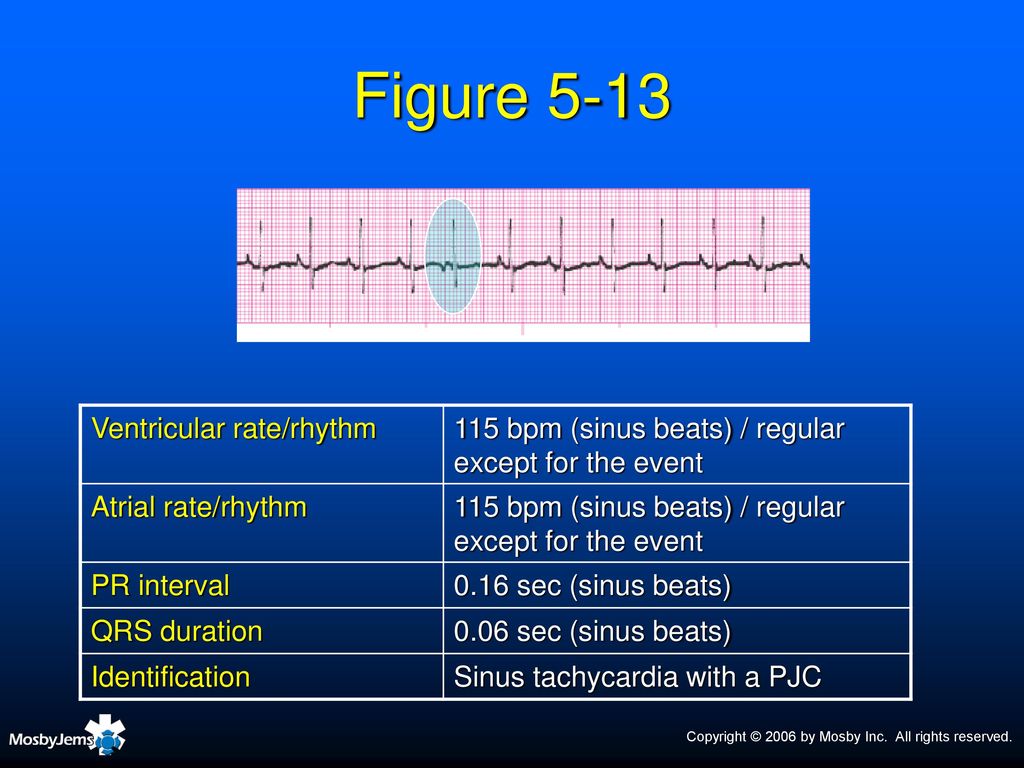
Normal Sinus Rhythm Sinus rhythm is the normal regular rhythm of the heart set by the natural pacemaker of the heart called the sinoatrial node It is located in the wall of the right atrium Normal cardiac impulses start there and are transmitted to the atria and down to the ventriclesSep 01, 07 · The rhythm in this tracing (shown in Figure 1 with the ventricular beats/ QRS complexes numbered on the lead II rhythm strip at the bottom) appears to be irregularly irregular If it were regularly irregular, several ECG diagnoses would move up in the differential diagnosis namely, normal sinus rhythm (NSR) with a regular bigeminal, trigeminalIdentify the rhythm • regular or irregular • rate • p wave • pr interval • qrs duration •eptopics / abnormalities sinus rhythm with premature junctional contraction • regular • 100 • normal – except for ectopic • 016 seconds • 012 seconds • pjc – 7th beat
Sinus Rhythm with PJC looks like sinus rhythm with a premature beat originating from the junction (no p wave or inverted p wave) Complex Test 2 ECG strips Treatment Cards 46 terms Cardiac Dysrhythmias 46 terms C D Adult 2 OTHER SETS BY THIS CREATOR 50 terms Dysrhythmia study guidePJC will have Inverted or hidden P wave Narrow 1' AV Block Regular That of Underlying Rhythm;7 Bigeminal PJCs 8 Sinus bradycardia with trigeminal PJCs 9 Sinus rhythm with trigeminal PJCs 10 Sinus bradycardia with a PJC at 600 AM
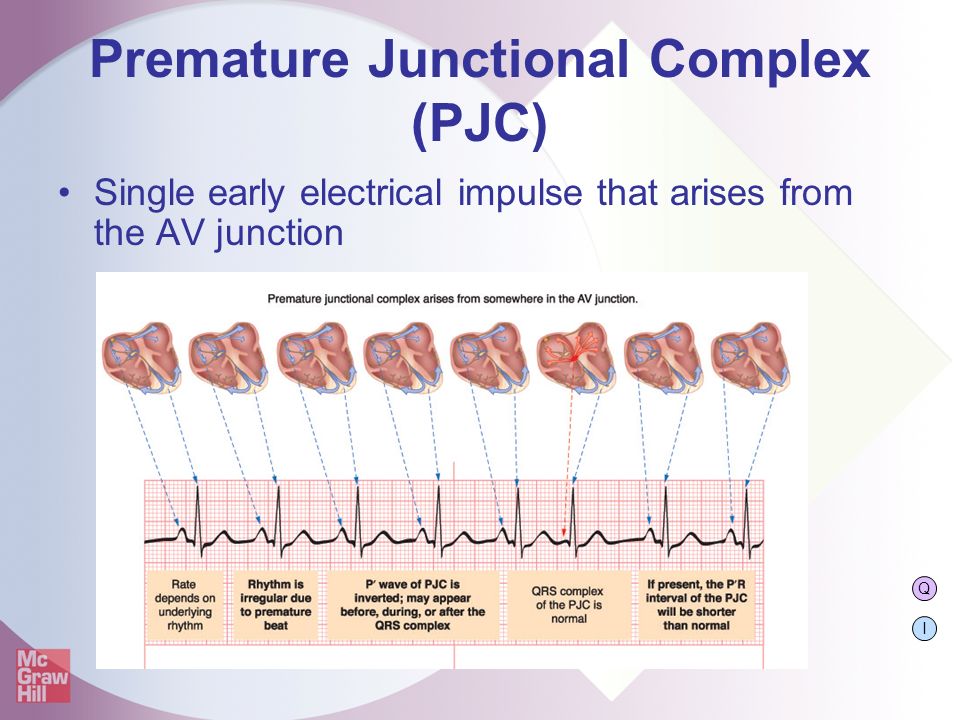
Rhythm ECG Characteristics Example Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Rate per minute Rhythm R R = P waves Upright, similar PR 012 0 second & consistent qRs 004 – 010 second PqRs 1P1qRs Sinus Tachycardia Causes Exercise Hypovolemia Medications Fever Hypoxia Substances Anxiety, Fear Acute MI Fight or FlightJun 04, 18 · A PJC is a beat that originates from the AV node junction, before a sinus beat, thus disrupting the underlying rhythm Typically there is either no pwave because it's hidden in the QRS complex, or the Pwave may be inverted and appear before the QRS complex Here's a picture of an ECG/EKG strip, showing 2 junctional beats (Source)Sinus rhythm the normal rhythm of the heart A rhythm is defined as three consecutive heart beats with identical waveforms on the ECG The similarity of the waveforms indicates that the origin of the impulse is the same The sinoatrial (SA) node is the heart's pacemaker under normal circumstances and the rhythm is referred to as sinus rhythmHence, sinus rhythm is the normal rhythm




Pin On Icu




Ekg Flash Cards Pdf Rhythm Ecg Characteristics Normal Sinus Rhythm Nsr Rate 60 100 Per Minute Rhythm R R P Waves Upright Similar P R 0 12 0 Course Hero
Impulses arise from sinus node Normal Pw axis 0° to 75° Normal Pw morphology Upright in I, IIaVF Inverted in aVR Upright or biphasic (positivenegative) in III, aVL, V1V2 Same morphology throughout rhythm strip Regular PP interval varying by less than 160 ms or less than 10 percentA sinus rhythm is any cardiac rhythm in which depolarisation of the cardiac muscle begins at the sinus node It is characterised by the presence of correctly oriented P waves on the electrocardiogram (ECG) Sinus rhythm is necessary, but not sufficient, for normal electrical activity within the heart The term normal sinus rhythm (NSR) is sometimes used to denote a specific type of sinusSinus Rhythm with PVCs for an ECG machine This video is provided by Cascade Healthcare Services, A leading provider of healthcare training courses including




Ekg Practice Flashcards Quizlet




Junctional Rhythms Boss Rn
Jan 02, 18 · Normal sinus rhythm Normal sinus rhythm is defined as the rhythm of a healthy heart It means the electrical impulse from your sinus node is being properly transmitted In adults, normal sinusApr 09, 19 · Example ECG Patient 67yearold female presents with a feeling like her "heart is skipping a beat" Interpretation Sinus bradycardia, premature atrial complexes, otherwise normal – Ventricular rate 58 BPM – PR interval 180 ms – QRS duration 84 ms – QT/QTc interval 402/394 ms – PRT axes 45 4 28 Key Points from Example ECGJun 08, 21 · ECG features Default heart rhythm;



Nt Prophecyhealth Com Docs Manuals Foundations Of Ecg Interpretation1 Pdf



Ekg Oct 26 30
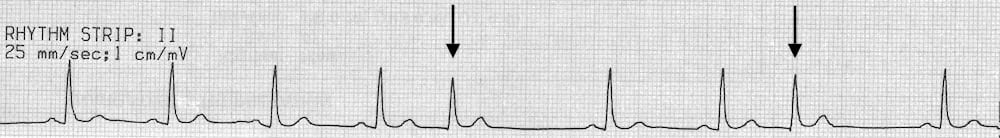
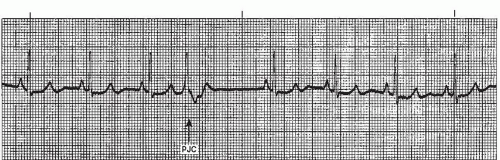
Jul 08, · An EKG strip with sinus bradycardia would show a regular heart rhythm, with consistent distances between both R waves and P waves P waves will be upright with a smooth and consistent appearance PR intervals will be of normal duration, the QRS complexes will be narrow, and there will be only one P wave for each QRS complexThis strip shows a nice sinus rhythm clipping along at 80 BPM The cadence of the ventricular complexes is broken up by a premature complex that is narrow and similar in morphology to the rest of the complexes This is obviously a PJCAnalyzing a Rhythm Strip Heart Rate –Methods of calculation 1 Six second count Barill, T (12) The Six Second ECG, A Practical Guide to Basic and 12 Lead ECG



Junctional Arrhythmias And Av Blocks Thoracic Key




Float Nurse Ekg Rhythm Strips 24 Ectopic Beats
Jan 02, 17 · EKG Rhythms Interpretation can be tricky especially when it comes to the uncommon ones With enough understanding of distinct features of each rhythm, it becomes an easy and fun task This is a detailed ECG guide with practice quiz and strips to help you master EKGFeb 12, 13 · Another clue that this is sinus is that the machine says it is sinus (read the top of the strip) We can see that it's rock solid across the early rhythm, then the PJC has a little less amplitude, and the next sinus beat (after the long pause and subsequent higher preload) has a higher amplitude Sinus rhythm @ 70 bpm with aRhythm analysis indicates normal sinus rhythm (NSR) at 68 bpm Premature atrial complexes (PACs), Premature junctional complexes (PJCs), and Premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) are present This encounter shows a normal sinus rhythm with a large amount of ectopy This causes an irregular looking rhythm that can easily confuse beginner monitor techs




Junctional Rhythms Boss Rn




Premature Supraventricular Complexes Basic And Bedside Electrocardiography 1st Edition 09
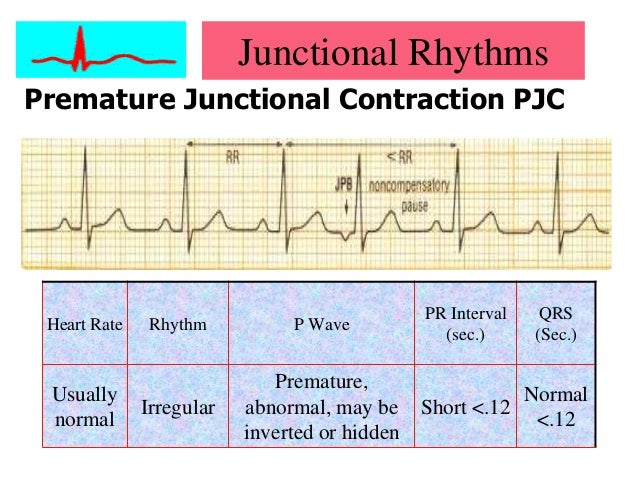
Rhythm Regularity Rate P Waves QRS Complex Premafure Junctional Contraction (PJC) Usually Regular with Isolated Anomaly That of Underlying Rhythm That of Underlying Rhythm;ECG • 12 lead ECG • ECG strip (Rhythm strip)(Rhythm strip) ECG • 12 ldECGlead ECG ECG t i Varying Rhythm sinus arrhythmia, Wandering pacemaker AFpacemaker, AF Extra Beats and Skips B PJC C PVCC PVC Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) • From SA node (sinus node)From SA node (sinus node)May 27, 16 · 02 e Sinus rhythm with a PJC 03 b Atrial flutter 04 a Sinus rhythm with ventricular bigeminy 05 d Sinus rhythm with PACs 06 c Supraventricular tachycardia with a PVC 07 e NSR with a PVC 08 b Atrial fibrillation with slow ventricular response 09 a Sinus rhythm with inverted T waves 10 a Sinus arrhythmia 11 c Sinus tachycardia




Dysrhythmia Interpretation And Management Ppt Download




Bigeminy Wikipedia
(A) "Sinus rhythm with ectopy" means a patient in sinus rhythm is also having Premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) Premature atrial contractions (PACs) Both PACs and PVCs (and sometimes PJCs)Telemetry Interpretation The following rhythm strips are for your practice We suggest you practice with these prior to taking the post test (All strips are sixsecond strips unless otherwise indicated) Rhythm Strip #1 ECG CriteriaBasic ECG Rhythm Interpretation Objectives At the completion of this course the learner will be able to 1 Identify the sequence of normal electrical activation of the heart 2 Describe the physiology of cardiac muscle contraction 3 Given a rhythm strip, identify Sinus, Atrial, Junctional and Ventricular dysrhythmias, and Atrioventricular Blocks 4




Ecg Learning Center Test




Premature Junctional Complex Pjc Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis
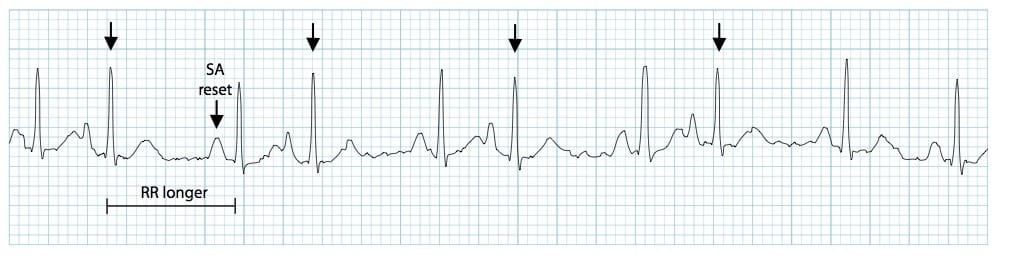
Ventricular Escape Rhythm (Idoventricular Rhythm) This rhythm is characterized by a heart rate usually between 30 to 40 bpm but may be lower than 30 An escape rhythm refers to the "automatic" or "escape" pacemaker of the heart located in the bundle branches, Perkinje network, or ventricular myocardiumThe ECG strip shows intermittent sinus slowing with two junctional escapes click here to view Junctional Escape Rhythm This is a sequence of 3 or more junctional escapes occurring by default at a rate of 4060 bpm There may be AV dissociation or the atria may be captured retrogradely by the junctional pacemaker2 Upsets the timing of the sinus node discharge, and the underlying rhythm will not resume on time following the pause C Criteria 1 Rhythm irregular – the underlying rhythm does not resume on time following the pause 2 Heart rate can be normal, 60 100 or slow, 40




Introduction To Telemetry Monitoring For Arrhythmias Nursing Ce Course Nursingce



Junctional Dysrhythmias Ppt Video Online Download
When the monitor is calibrated to a paper speed of 25mm per second, each of these represents 004 seconds The normal PR interval is less than five small squares and the QRS complex is less than three small squares Normal sinus rhythm is shown in Fig 2 (on article PDF) How to read a rhythm stripSinus Rhythm Types The dysrhythmias in this category occur as a result of influences on the Sinoatrial (SA) node Rhythms in this category will share similarities in a normal appearing P wave, the PR interval will measure in the "normal range" of 012 – 0 second, and the QRS typically will measure in the "normal range" of 006 – 010 secondStart studying EKG Strips Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools Home Browse Normal Sinus Rhythm with one PJC Sinus Bradycardia with one PJC Junctional Rhythm Accelerated Junctional Rhythm ACLS Rhythm Strips terms bethanysegovia EKG questions 29 terms tobin_garner



Chicago Medicine Uic Edu Wp Content Uploads Sites 6 17 06 Ekg 2 Lead Interp Refresher Pdf




Ecg Rhythms Several Tricks Of A Pjc In One Strip
Mar , 21 · Sinus Rhythm with Other Disturbances When we speak about normal sinus rhythm, the adjective "normal" refers only to heart rhythm, it does not mean that the complete EKG is normal For example, normal sinus rhythm can be described in the presence of bundle branch block or signs of acute myocardial infarct It is a different matter when an initial sinus rhythmAug 01, · PACs arising close to the AV node ("low atrial" ectopics) cause retrograde activation of the atria, producing an inverted P wave with a relatively short PR interval ≥ 1 ms (PR interval < 1 ms is classified as a PJC)May 17, 17 · ECG Basics Accelerated Junctional Rhythm Overriding Normal Sinus Rhythm This strip shows a junctional rhythm at a rate of 110 beats per minute The QRS complexes are slightly wide at 10 seconds (100 ms), and they are within the parameters for supraventricular rhythm The term, "junctional tachycardia" could be used, also, but this is not



Www Nursingcenter Com Wkhlrp Handlers Articlecontent Pdf Key Pdf




Ekg Rhythms From Order To Chaos
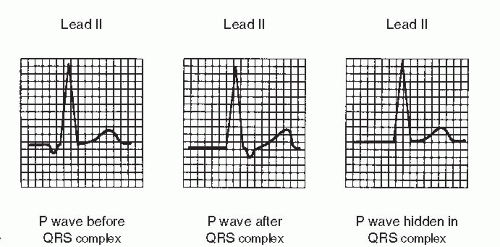
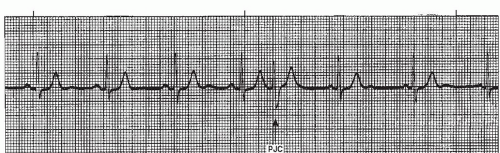
Sinus Rhythm with a Premature Junctional Contraction (PJC) The same statements made regarding PAC's can be repeated for PJC's These are typically considered benign, but can be a signal that something serious is going on Notice in this example that the ectopic junctional beat does not display a P waveInterpretation Normal sinus rhythm with one PJC A PJC is an early beat that originates in an ectopic pacemaker site in the atrioventricular (AV) junction, interrupting the regularity of the basic rhythm, which is usually a sinus rhythm Like the premature atrial contraction (PAC), the PJC is characterized by a premature, abnormal P wave followed by a normal duration QRS complex andSinus rhythm means a normal heart beat, both with respect to the heart rate and rhythm Heart rate will fall between 60 and 100 beats per minute The shape of the electrocardiogram (EKG) tracing will exhibit certain key attributes to be considered normal, as discussed below



Utmc Utoledo Edu Depts Nursing Pdfs Advanced ekg refresher Pdf



Ekg Oct 26 30
One P wave for each QRS Complex NarrowSinus rhythm with a PJC PQRS ratio 11, except in event This strip shows a nice sinus rhythm clipping along at 80 BPM The cadence of the ventricular complexes is broken up by a premature complex that is narrow and similar in morphology to theSinus Rhythm W / ST Depression and PJC K Junctional Tach @ 100 bpm L 7 Sinus Rhythm W/ PVC M Sinus Rhythm W/ multifocal PVC'S N Monomorphic VTach O 8 the EKG The diagnosis of BBB is based primarily on the width and appearance of the QRS Ask these three questions 1 Is the QRS wide (> 012 seconds)



Cardiac Arrythmias




Sr With Pjc Youtube
Usually 60 to 100 Positive;The ECG strip shows intermittent sinus slowing with two junctional escapes Junctional Escape Rhythm A Junctional Escape Rhythm is a sequence of 3 or more junctional escapes occurring by default at a rate of 4060 bpmBasic EKG Test (100 strips) 01 Identify the following rhythm a Sinus bradycardia b Accelerated junctional rhythm c Sinus rhythm with 1st degree block d



1




Pin On Nurse Life
PR Interval more that0sec;Rhythm Strip Flash Card Practice 1 Sinus Brady Arrhythmia The rate is slow and the rhythm is irregular 2 Sinus Brady heart rate is less than 60 3 Normal Sinus Rhythm 4 Normal Sinus Rhythm 5 Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) Narrow complex tachycardia 6 Sinus Tachycardia heart rate greater than 100 7 Normal Sinus RhythmJul 18, 11 · Standard ECG paper is composed of small squares;




Ekg Interpretation Cheat Sheet Heart Arrhythmias Guide Update



My Methodistcollege Edu Ics Icsfs Mm Junctional Rhythm Resource Pdf Target 5a5551 09a5 4fef ef E9d1418db53a
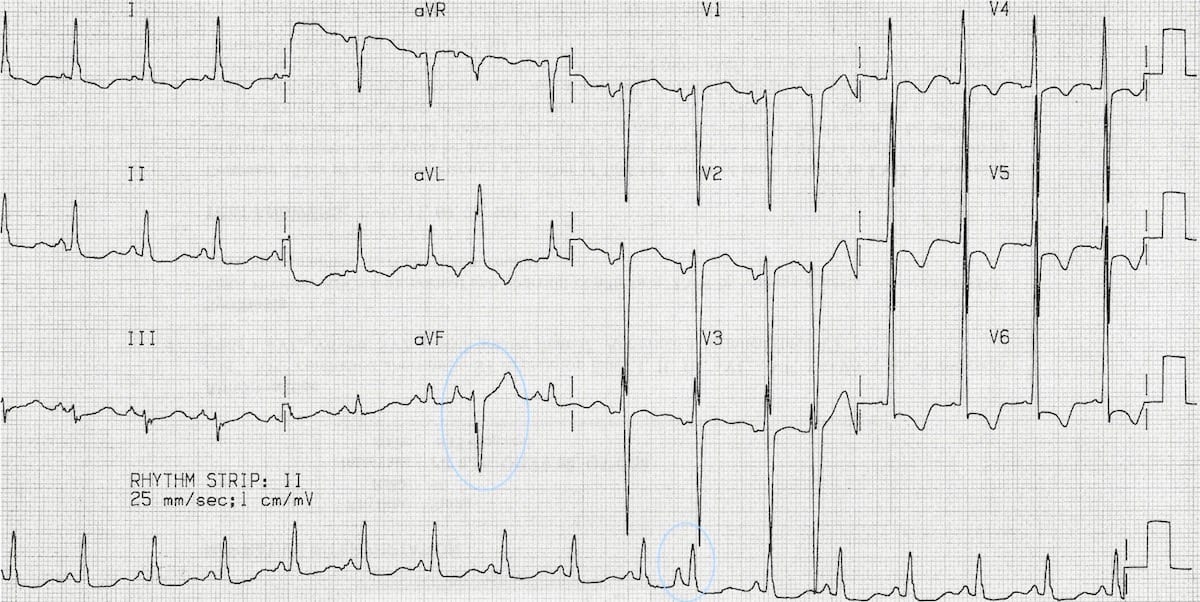
A compensatory pause implies that the sinus beat after the premature beat occurs on schedule, such that there is two sinus cycles (2 RR intervals) between the beats before and after the premature beatThis is the hallmark of ventricular premature beats Variants of premature atrial contractions Should the premature atrial impulse reach the atrioventricular node or bundle of




Sudden Onset Of Svt Rhythm Regular Vertigo Treatment



Cardiac Arrhythmias



Junctional Arrhythmias And Av Blocks Thoracic Key



Premature Atrial Complex Pac Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis




Float Nurse Ekg Rhythm Strip Quiz 17




Pac Pjc Pvc Pdf 5 Minute Speedy Session Telemetry Pac Pjc Pvc Sinus Rhythm Just A Baseline To Compare To The Other Strips Notice That Every P Wave Has Course Hero



Q Tbn And9gcsztx Yiup6dgjcscknsguogls0mjbhalqbp1auz2 K1yzjb3ef Usqp Cau



Silo Tips Download By The End Of This Continuing Education Module The Clinician Will Be Able To




Ecg Rhythms Several Tricks Of A Pjc In One Strip



Basics Of Electrocardiography Arrhythmia Pacemaker




Chapter 2 For 12 Lead Training Rhythm Practice Ppt Download




Ekg Rhythm Strips Final Test Flashcards Quizlet




Ecg Educator Blog Premature Junctional Complex Pjc



Junctional Arrhythmias And Av Blocks Thoracic Key



Premature Atrial Contraction Electrocardiogram Wikidoc




Sr With Pjc Youtube



Premature Junctional Complex Pjc Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis



Rhythm Card Wordpress Com




Ecg Rhythms Several Tricks Of A Pjc In One Strip



Www Jstor Org Stable




Float Nurse Ekg Rhythm Strips 24 Ectopic Beats




Premature Junctional Complex Pjc Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis



Medcram Ekg Course




Ecgrhythms What Is A Normal Sinus Rhythm




Ectopic Complexes And Rhythms Thoracic Key




Name That Strip Article Nursingcenter




Premature Junctional Complex Pjc Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis



Ekg Oct 26 30




Float Nurse March 19



Chicago Medicine Uic Edu Wp Content Uploads Sites 6 17 06 Ekg 2 Lead Interp Refresher Pdf




Ekg Medic Rhythms Atrial And Vent Flashcards Quizlet




Premature Supraventricular Complexes Basic And Bedside Electrocardiography 1st Edition 09




Premature Supraventricular Complexes Basic And Bedside Electrocardiography 1st Edition 09



Http Www Rcpals Com Downloads Aclsrhythmreviewaug02ak Pdf




Ecg Learning Center An Introduction To Clinical Electrocardiography




Advanced Assessment Ecg Interpretation Version 14 Obhg Education




Matters Of The Heart Junctional Rhythms And Beats Patmac Rn



Lesson V Ecg Rhythm Abnormalities



Http Www Bremss Org Uploadedfiles File Ekg Intermediate Tips Tricks Tools Pdf



Rhythm Strip Review



Practice Rhythms Strips Ppt Download



Premature Atrial Complex Pac Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis



Junctional Arrhythmias And Av Blocks Thoracic Key




Premature Supraventricular Complexes Basic And Bedside Electrocardiography 1st Edition 09



Utmc Utoledo Edu Depts Nursing Pdfs Advanced ekg refresher Pdf




Ecg Review Bigeminal Term Misuse 03 12 01 Ahc Media Continuing Medical Education Publishing




Ecg Learning Center An Introduction To Clinical Electrocardiography




Ecg Learning Center An Introduction To Clinical Electrocardiography




Ecg Rhythms Sinus Rhythm With Long Pri Mimicking Junctional Rhythm



1




Pin On Life Of A Nurse




Ecg Educator Blog Premature Junctional Complex Pjc



Chicago Medicine Uic Edu Wp Content Uploads Sites 6 17 06 Ekg 2 Lead Interp Refresher Pdf




Pin On Cardiac




Basic Arrhythmia Handout Oakwood Healthcare System



Practice Rhythms Strips Ppt Download



Ekg Oct 26 30



Ekg Rhythms Interpretation Best Practice Quiz Strips Acls



Http Www Nwcemss Org Assets 1 System Entry Junctional Rhythms F16 Pdf




Ekg Rhythms Part 2 Flashcards Quizlet




Practice Test Only Dysrhythmia Interpretation Therapeutic Modalities Pdf Free Download




Ecg Learning Center An Introduction To Clinical Electrocardiography



1




Advanced Assessment Ecg Interpretation Version 14 Obhg Education




Ecg Interpretation Ecg Interpretation Review 69 Pvc Pjc Retrograde Concealed Conduction Group Beating




Premature Atrial Contraction Electrocardiogram Wikidoc



Silo Tips Download By The End Of This Continuing Education Module The Clinician Will Be Able To




Ecg Interpretation Ecg Interpretation Review 69 Pvc Pjc Retrograde Concealed Conduction Group Beating




Premature Atrial Complex Pac Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis




Name That Rhythm Ppt Video Online Download
.jpg)



Ecg Interpretation Ecg Interpretation Review 68 Pvc Interpolated Pvc Concealed Conduction Compensatory Pause




Ch 9 Flashcards Quizlet




Junctional Rhythms Boss Rn



Ekg Oct 26 30




Junctional Rhythms Flashcards Quizlet




Ecg Educator Blog Premature Junctional Complex Pjc


コメント
コメントを投稿